# VsCode配置STM32编译调试环境
【保姆】vscode配置单片机编译调试烧录环境(以STM32为例)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
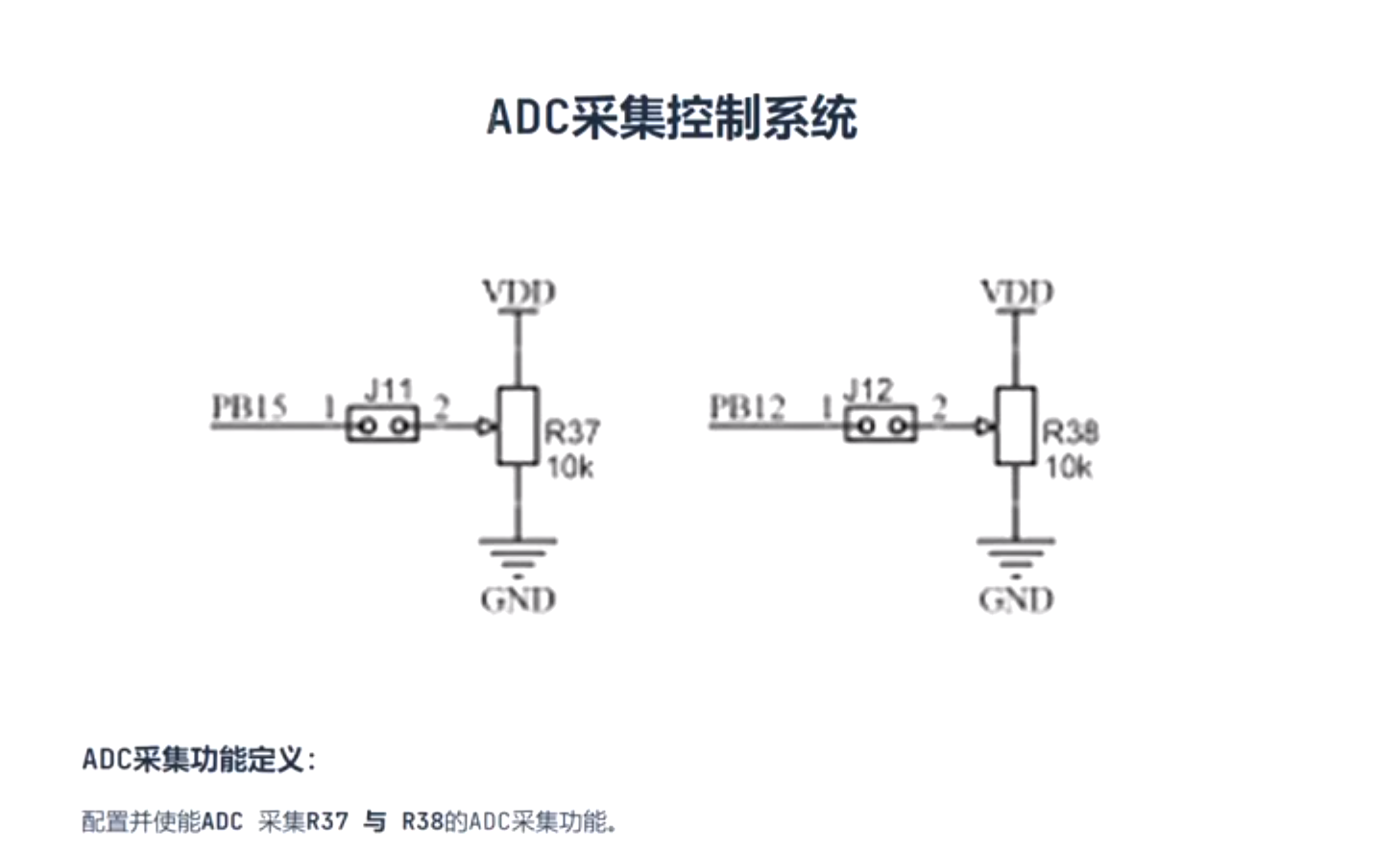
一、ADC采集系统
1. ADC通道(外部电路)

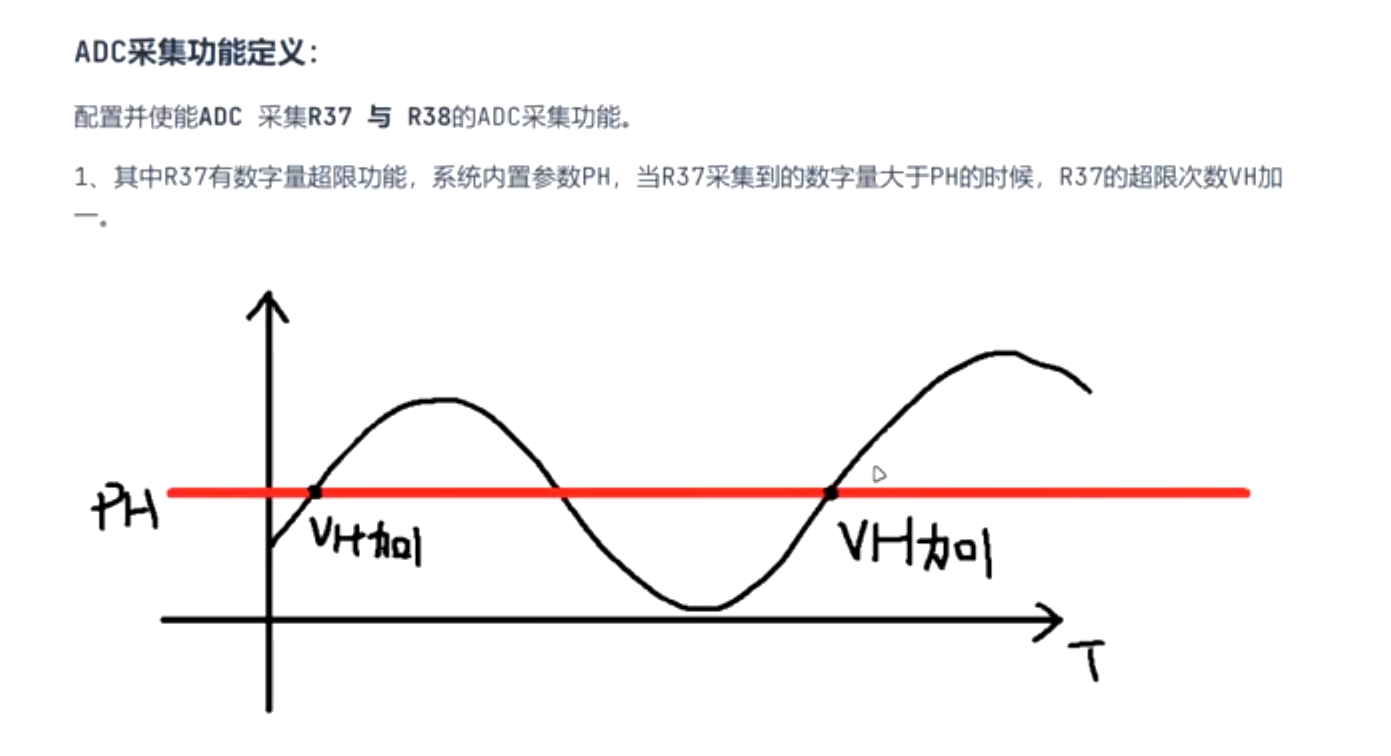
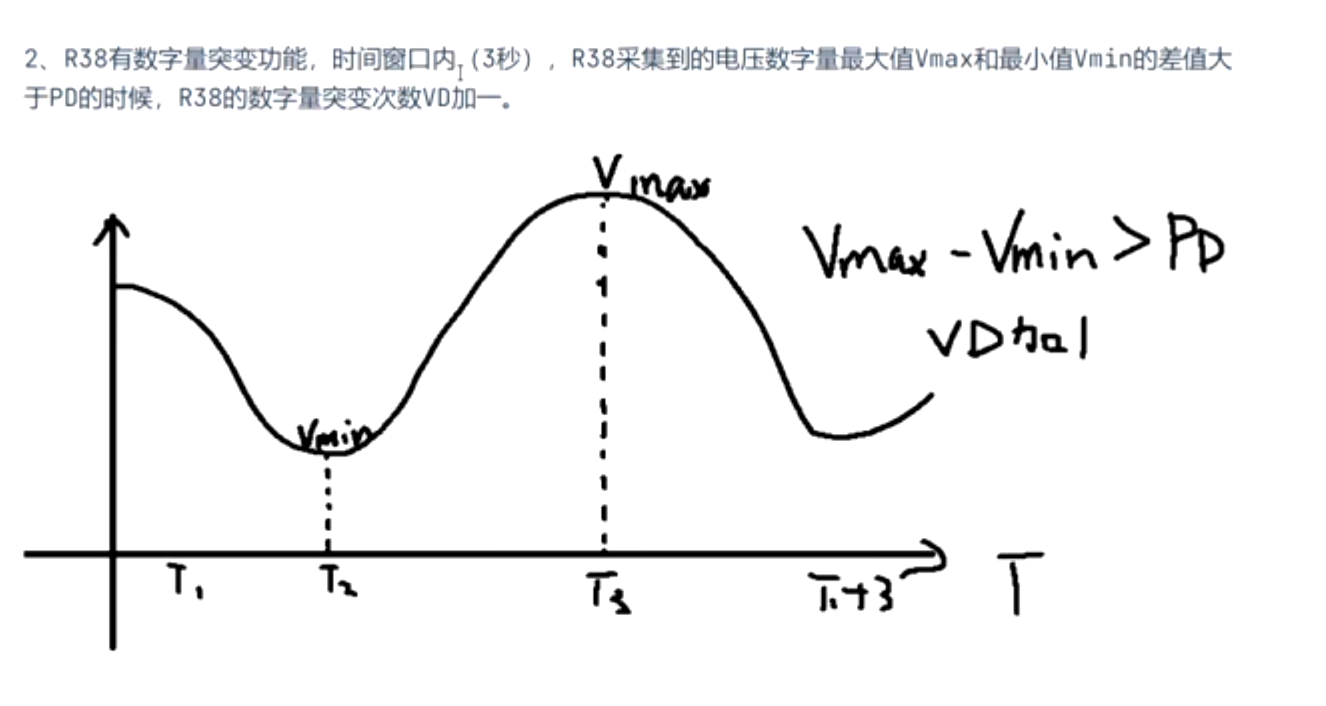
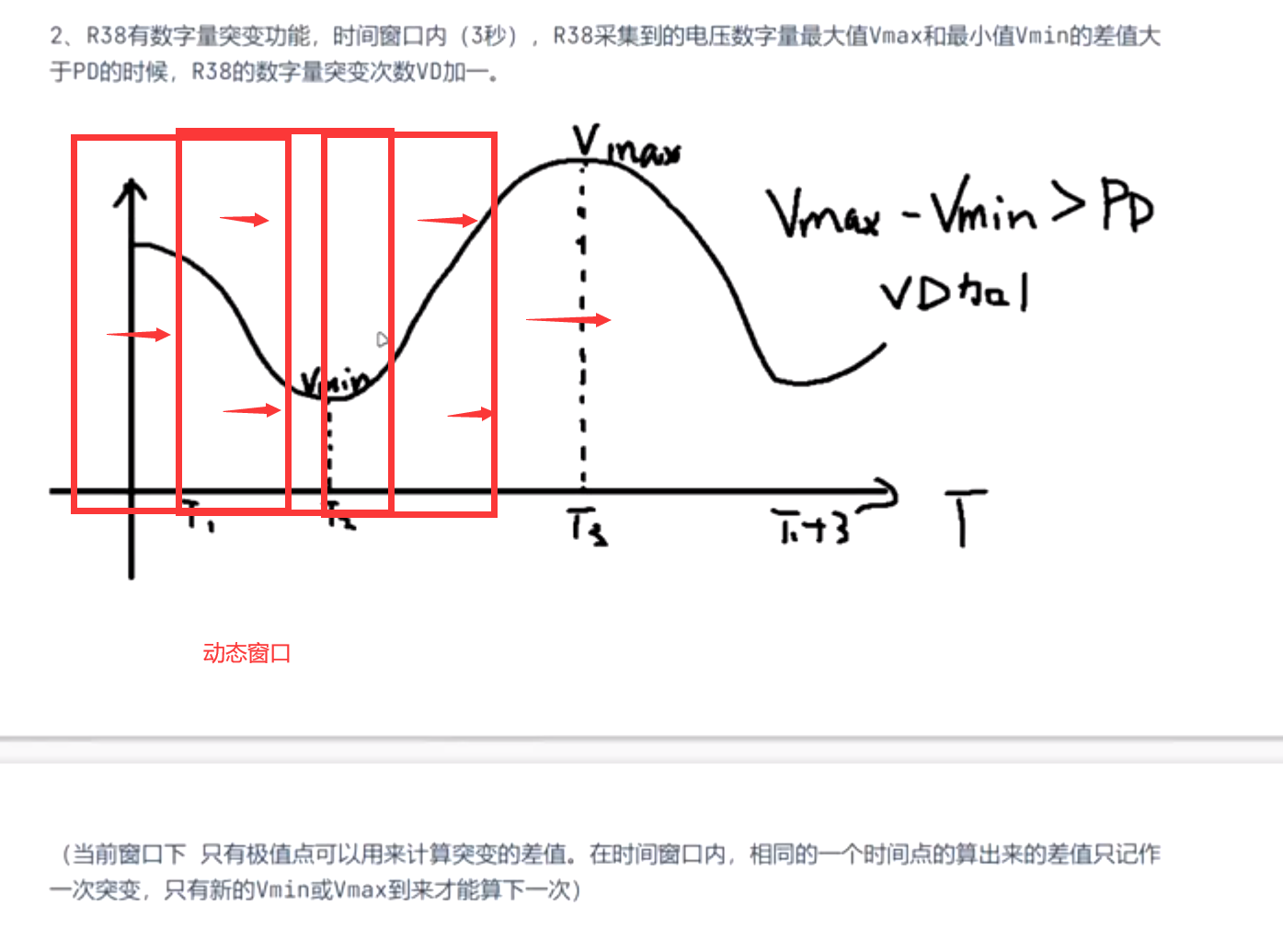
2. 功能要求

3. 动态窗口

"动态"的含义:3秒的实时采集窗口随着时间自行移动,adc采集的值动态实时更新在3s的窗口数据内

二、功能实现
1. ADC解算
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| uint32_t dma_buff[2][30];
float adc_value[2];
void adc_proc()
{
for(uint8_t i=0;i<30;i++)
{
adc_value[0] += (float)dma_buff[0][i];
adc_value[1] += (float)dma_buff[1][i];
}
adc_value[0] = adc_value[0] / (30+1);
adc_value[1] = adc_value[1] / (30+1);
}
|
2. LCD底层实现
2.1 变量定义
1
2
3
| uint8_t lcd_disp_mode;
uint16_t ph_value;
uint16_t pd_value;
|
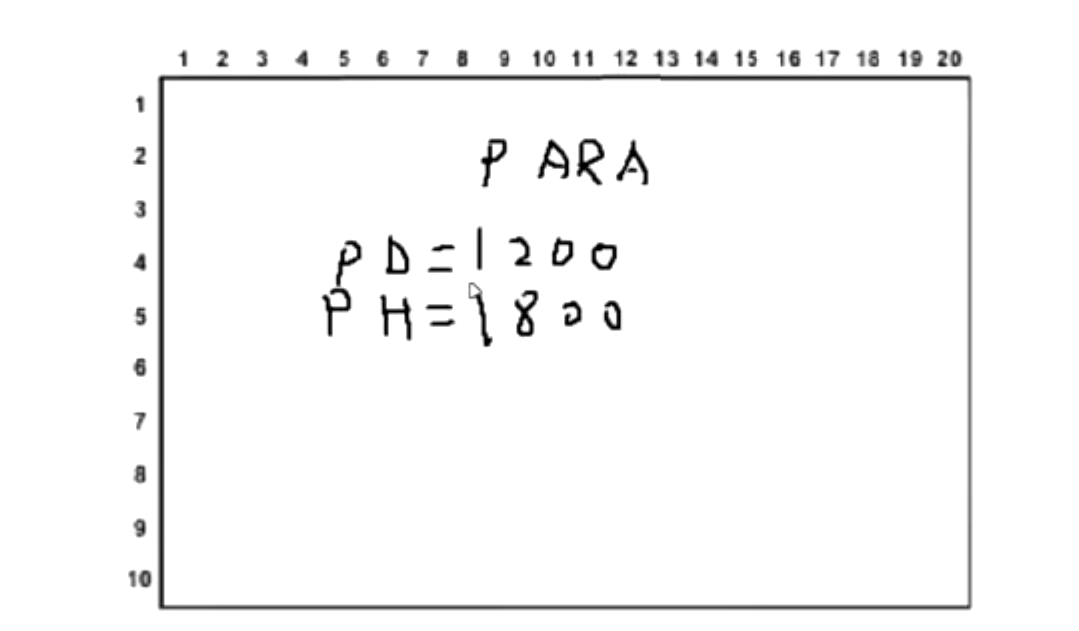
参数界面

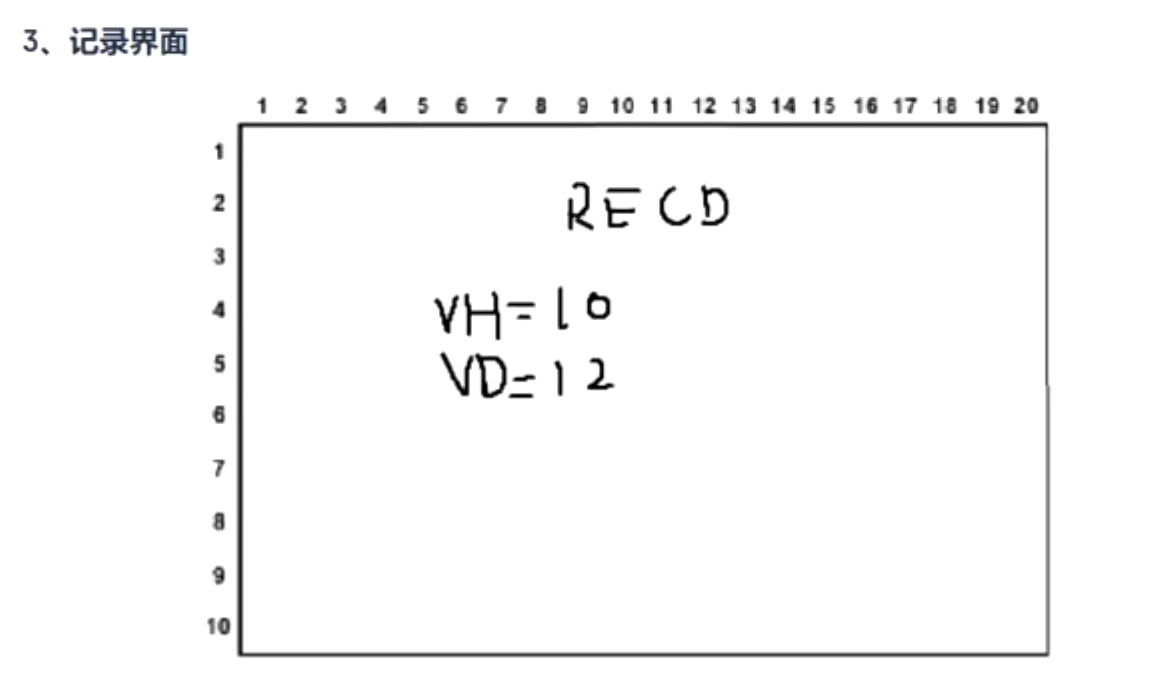
记录界面

2.2 LCD进程
由于4T官方提供的LCD底层驱动,当显示的数据位数增加时,显示的位数会增加,但是当位数减小时,却不能对旧的数据进行清空。
所以这里用“空格”来覆盖刷新,达到位数减小显示缩减的效果。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| void lcd_proc()
{
switch(lcd_disp_mode){
case 0:
LCD_Sprintf(Line1," DATA");
LCD_Sprintf(Line3," R37:%d ",(int)adc_value[0]);
LCD_Sprintf(Line4," R38:%d ",(int)adc_value[1]);
break;
case 1:
}
}
|
#LCD背光 问题
现象:如图所示,只有在对LCD写入的片段,LCD才有正常的背景

原因:未对LCD进行初始化清屏
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
system_init();
LCD_Init();
LCD_Clear(Black);
LCD_SetTextColor(White);
LCD_SetBackColor(Black);
scheduler_init();
|
来源:lcd.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
void LCD_Clear(u16 Color)
{
u32 index = 0;
LCD_SetCursor(0x00, 0x0000);
LCD_WriteRAM_Prepare();
for(index = 0; index < 76800; index++)
{
LCD_WR_DATA(Color);
}
}
|
2.3 LED功能和初始化状态

2.4 LCD底层完整代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| #include "bsp_system.h"
uint8_t lcd_disp_mode;
uint16_t ph_value = 2000;
uint16_t pd_value = 1000;
uint16_t vh_value;
uint16_t vd_value;
void LcdSprintf(uint8_t Line, char *format, ...)
{
char String[21];
va_list arg;
va_start(arg, format);
vsprintf(String, format, arg);
va_end(arg);
LCD_DisplayStringLine(Line, String);
}
void lcd_proc()
{
switch (lcd_disp_mode)
{
case 0:
LcdSprintf(Line1, " DATA");
LcdSprintf(Line3, " R37:%d ", (int)adc_value[0]);
LcdSprintf(Line4, " R38:%d ", (int)adc_value[1]);
break;
case 1:
LcdSprintf(Line1, " PARA");
LcdSprintf(Line3, " PH:%d ", ph_value);
LcdSprintf(Line4, " PD:%d ", pd_value);
break;
case 2:
LcdSprintf(Line1, " RECD");
LcdSprintf(Line3, " VH:%d ", vh_value);
LcdSprintf(Line4, " VD:%d ", vd_value);
break;
}
}
|
3. 按键底层
uwTick:在Systick(系统滴答定时器)中断中自增,可以用作单片机运行的时间戳
HAL库与Cubemx系列|Systick-系统滴答定时器详解-腾讯云开发者社区-腾讯云 (tencent.com)
3.1 按键处理进程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
| uint8_t ph_pd_flag;
void key_proc(void)
{
key_val = key_read();
key_down = key_val & (key_old ^ key_val);
key_up = ~key_val & (key_old ^ key_val);
key_old = key_val;
if (key_down == 3)
{
if (lcd_disp_mode == 1)
{
ph_pd_flag ^= 1;
}
else if(lcd_disp_mode == 2)
{
key_tick = uwTick;
}
}
if(key_up == 3)
{
if(lcd_disp_mode == 2)
{
if(uwTick - key_tick > 2000)
{
key_tick = 0;
vd_value = vh_value = 0;
}
}
}
switch (key_down)
{
case 4:
if (++lcd_disp_mode == 3)
{
lcd_disp_mode = 0;
}
break;
case 1:
if (lcd_disp_mode == 1)
{
uint16_t *p = (ph_pd_flag) ? &ph_value : &pd_value;
*p += 100;
if (*p > 4096)
{
*p = 4096;
}
}
break;
case 2:
if (lcd_disp_mode == 1)
{
uint16_t *p = (ph_pd_flag) ? &ph_value : &pd_value;
*p -= 100;
if (*p == 65536 - 100)
{
*p = 0;
}
}
break;
}
}
|
4. adc采集
4.1 变量定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| #include "adc_app.h"
uint32_t dma_buff[2][30];
float adc_value[2];
#define WINDOWS_SIZE 3000
adc_data_t adc_buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
int buffer_start = 0;
int buffer_end = 0;
uint8_t vd_flag;
|
4.2 添加数据到动态串口(缓冲区)
本例中,ADC采样的环形缓冲区比较特殊,具备动态时间窗口的特性
- 和一般的环形缓冲区一样,具备头指针和尾指针的概念,环形存取数据。
- 缓冲区具备“时间窗口”的概念,那么就要让缓冲区中最老的数据,存在时间不能超过三秒,超过则移除(实际上是写指针移位,相当于队这个无用的数据不再进行读取,环形缓冲区中读取数据,就相当于将这个数据移除缓存区,因为索引指针不会再指向这个数据。)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
void add_adc_data(uint32_t adc,uint32_t current_time,adc_data_t *buffer)
{
buffer[buffer_end].timestamp = current_time;
buffer[buffer_end].adc = adc;
buffer_end = (buffer_end + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE;
if(buffer_end == buffer_start)
{
buffer_start = (buffer_start + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE;
}
while((current_time - buffer[buffer_start].timestamp > WINDOWS_SIZE))
{
buffer_start = (buffer_start + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE;
}
}
|
4.3 检查缓冲区的突变
对当前窗口进行极大值,极小值的检测。
注意区分极大值,极小值和最大值最小值的区别。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
void check_adc_sudden_change(uint16_t *sudden_change_count,adc_data_t *buffer)
{
uint16_t f_max = buffer[buffer_start].adc;
uint16_t f_min = buffer[buffer_start].adc;
int index = buffer_start;
while(index != buffer_end)
{
if(buffer[index].adc > f_max)
{
f_max = buffer[index].adc;
}
if(buffer[index].adc < f_min)
{
f_min = buffer[index].adc;
}
index = (index + 1) % BUFFER_SIZE;
}
uint16_t diff = f_max - f_min;
if(diff < pd_value)
{
vd_flag = 1;
}
else if(vd_flag == 1)
{
vd_flag = 0;
(*sudden_change_count) ++;
}
ucLed[2] = (diff > pd_value)?1:0;
}
|
4.4 ADC解析进程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| void adc_proc()
{
uint32_t Time_tick = HAL_GetTick();
static uint8_t vh_flag;
for(uint8_t i=0;i<30;i++)
{
adc_value[0] += (float)dma_buff[0][i];
adc_value[1] += (float)dma_buff[1][i];
}
adc_value[0] = adc_value[0] / (30 + 1);
adc_value[1] = adc_value[1] / (30 + 1);
add_adc_data(adc_value[0],Time_tick,adc_buffer);
check_adc_sudden_change(&vd_value,adc_buffer);
if(adc_value[1] < ph_value)
{
vh_flag = 0;
}
else if(vh_flag == 0)
{
vh_flag = 1;
vh_value++;
}
}
|
5. LED底层
5.1 LED显示进程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
void led_proc(void)
{
ucLed[0] = (lcd_disp_mode == 0);
ucLed[1] = adc_value[1] > ph_value ? 1 : 0;
led_disp(ucLed);
}
|
6. 串口通信
6.1 串口通信进程
sscanf:
sscanf 是一个格式化输入函数,主要用于从字符串中提取数据。- 它按照指定的格式读取输入字符串,并将解析后的数据存储到指定的变量中。
- 语法:
int sscanf(const char *str, const char *format, ...)
strcmp:
strcmp 是一个字符串比较函数,用于比较两个字符串是否相等。- 它返回一个整数,表示两个字符串的字典顺序。
- 语法:
int strcmp(const char *str1, const char *str2)
- 返回值:
- 小于 0:
str1 小于 str2
- 等于 0:
str1 等于 str2
- 大于 0:
str1 大于 str2
总结:
sscanf:将stream内容取出,并根据入口参数的格式化过滤内容,取出数据
strcmp:比较两个字符串的内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| void uart_proc(void)
{
if(ringbuffer_is_empty(&usart_rb)) return;
ringbuffer_read(&usart_rb, usart_read_buffer, usart_rb.itemCount);
uint16_t value;
uint16_t *p = NULL;
if(sscanf((const char*)usart_read_buffer,"$PD(%hu)",&value) == 1)
{
p = &pd_value;
}
else if(sscanf((const char*)usart_read_buffer,"$PH(%hu)",&value) == 1)
{
p = &ph_value;
}
else if(strcmp((const char*)usart_read_buffer,"#VH") == 0)
{
printf("VH:%d\n",vh_value);
}
else if(strcmp((const char*)usart_read_buffer,"#VD") == 0)
{
printf("VD:%d\n",vd_value);
}
if(value < 4096)
{
*p = value;
}
memset(usart_read_buffer, 0, sizeof(uint8_t) * BUUFER_SIZE);
}
|



![【stm32单片机】[操作系统][RT-Thread][3]线程通信](/img/blog_cover/rt-thread.jpg)